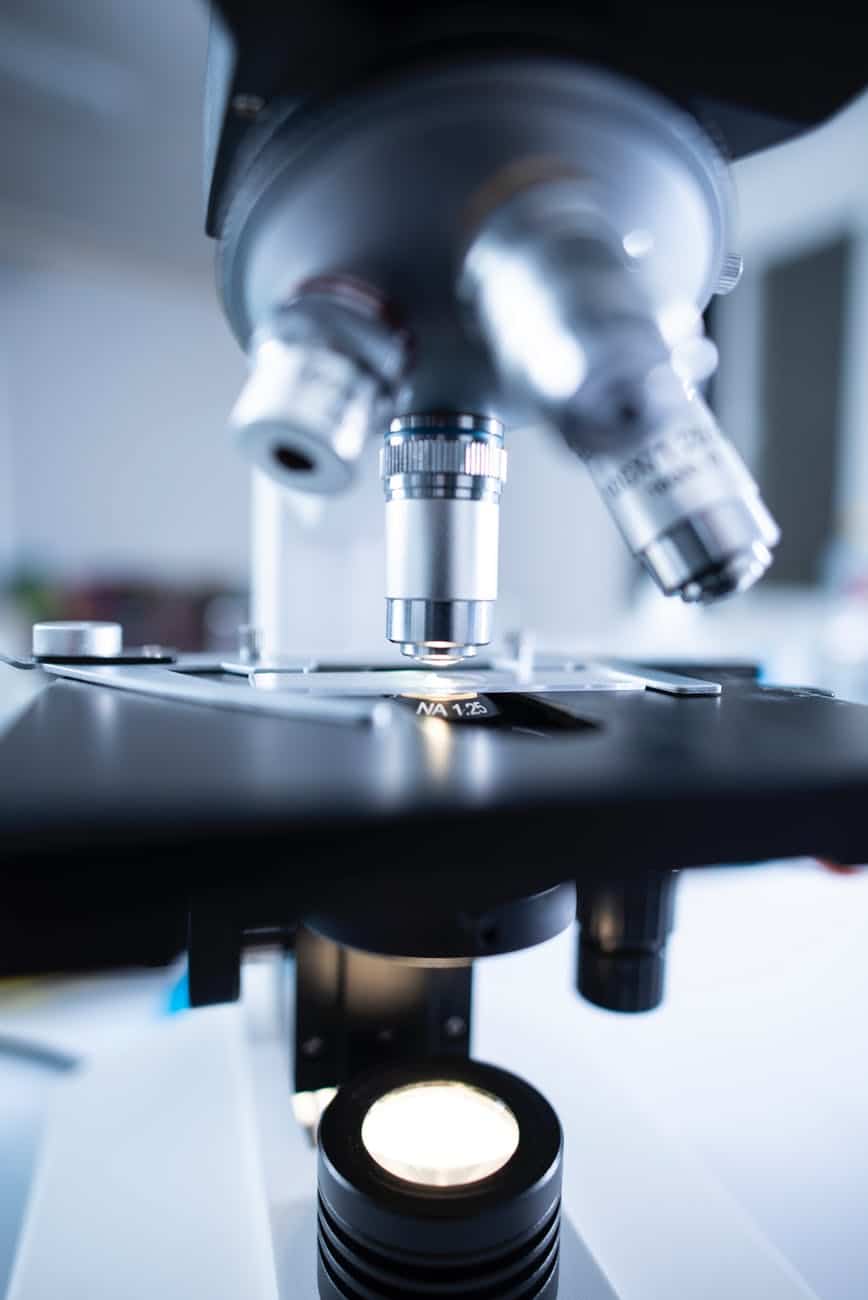
Microscopes are amazing because they allow us to see things invisible to the eyes! Let’s see how to use a microscope and how does it work. Since their invention in the 17th century, they allowed countless biological observations and have led to major scientific discoveries. Among other things, microscopes unveiled the anatomy of the cell and the incredible world of micro-organisms. The first microscopes where optical microscope or light microscope, but they have since evolved to give rise to much fancier microscopy techniques!
Table of Contents
How does a microscope work?
The general principle of an optical microscope is that the light will penetrate the sample and create an image projected on the ocular lens. In details, a microscope uses a light source (mostly LED now) and a condenser to make the light to converge towards the sample. The light will then enter the objective lens, which accounts for most of the magnification. In a compound microscope, the light still has to go through a second lens called the ocular lens. As a result, the magnification capacity of both lenses is multiplied. Please have a look at my previous posts to find the best compound microscopes for beginners or to find the best kits of prepared microscope slides for kids and students.
The ocular lens is typically a 10x or 20x magnifying lens. On the other hand, the rotating objective lenses allow you to select the desired magnification. Generally, objective lenses are either 4x, 10x or 40x (and even 63x or 100x on more advanced microscopes using oil). Therefore, the highest magnification using a standard microscope is 400x. You remember why? This is because the 10x objective is multiplied by the 40x objective. This means that you will be able to see an object 400 times its real size!
You can also find affordable microscopes with a magnification capacity ranging up to 2000x! As a comparison, a human hair is approximately 0.07mm thick (1/400 inch) and under this microscope it would appear as if it was 14cm (5.5 inches) at 2000x!
Click Here To See The OMAX 40X-2000X Lab LED Binocular Microscope on Amazon
How to use a microscope?
Using a microscope is easy, but the difficult part is to obtain the perfect view of your specimen. To facilitate the observations, you can first adjust the light intensity. Then, you can adjust the focus by turning the macro or micro knob. The macro knob is the biggest and allows coarse changes to the focus. On the other hand, the micro knob allows fine tuning of the focus. A simple way to find the right focus is to use a glass slide with a trait of wax crayon. It will make the adjustments easier and then you can switch to another specimen and only have to fine tune the focus.
Specimen preparation for microscopy
Even though you can observe a specimen directly on a glass slide under the microscope, maintaining the integrity of the sample as well as a good contrast can be difficult. In order to examine specimen such as cells under a microscope, there are a few steps that will help to have a better view and to facilitate manipulations.
Check these glass slides for microscopy on Amazon
Fixation
First, the specimen can be fixed. The goal of this process is to maintain the integrity of the cell by increasing its rigidity. This is achieved by treating the cells with ethanol (alcohol), methanol and also formaldehyde. In addition to the conservation of the cellular shape, it will efficiently fix the cell to the glass slide.
Permeabilization
This step is required if you want to use a staining that is unable to penetrate the cell. By using a mild detergent, you can generate small holes in the cellular membranes. As a result, the membrane will become permeable to different types of staining.
Staining
There is a huge variety of staining used both for medical and research laboratories. These dyes can be used to stain different component of the cell such as the nucleus or the cellular membrane. Some dyes are also used in combination in order to differentiate different type of cells within a tissue. An example of that is the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. The hematoxylin will stain the nucleus in blue whereas the eosin will stain the cytoplasm in pink. This staining method enables the easy identification of red blood cells and muscle cells within a tissue sample.
If you want to experiment at home and stain cell samples, there are easier method that you can try. For example, you can use food colorants to stain cells. Although this is not a specific type of colorant, it will increase the contrast of the sample and you will obtain better images. You could also try iodine, but be cautious because of the toxicity of this substance! Iodine has the capacity to stain starch in dark blue. It can be used as a staining method for cells in order to make the nucleus more visible.
For more information about staining methods and their use please check this Wikipedia page.
Mounting
To mount the specimen on a glass slide for microscopy, it is recommended to use a cover slip. This glass cover will protect the specimen and prevent its degradation. This way you can conserve your precious slides for further eventual observations.
Ideas for experiments using a microscope
There are many simple experiments that you can do with a microscope. First, you can take some water in a pond or a lake and look at the micro-organisms present in the water. You can also look at your own cells by scratching the inner side of your cheek with a toothpick and putting it on a slide. Finally, another cool thing is to look at vegetal cells by using a thin layer of onion skin. Have fun discovering the microscopic world!
Check my previous posts find the best compounds microscopes for kids and beginners. See also how create a colorful rainbow with the dispersion and refraction of light through a prism or find out how to generate electricity with a thermoelectric Peltier generator.